

EtherNet/IP® is an open network using Ethernet. As with DeviceNet®, EtherNet/IP® is managed by ODVA (formerly Open DeviceNet Vendors Association, Inc.). This network can be used at the controller and device levels and alongside general-purpose Ethernet.
The network environment can be built based on general-purpose Ethernet. The maximum cable length between nodes (or Ethernet switches) is 100 m (328.1′). There is no limit on the total extension distance. Up to 256 nodes can be connected. General-purpose Ethernet communication can be used on the same network.
Communication is performed using TCP/IP and the Common Industrial Protocol (CIP), which are communication protocols that use standard Ethernet technologies. CIP is a communication protocol used by various networks such as DeviceNet®, ControlNet, and CompoNet. General-purpose Ethernet communication can be used on the same network. EtherNet/IP® can communicate using well-known ports and thus can give priority to EtherNet/IP® communication by using Ethernet switches that support the Quality of Service (QoS) function, which increases the communication speed.
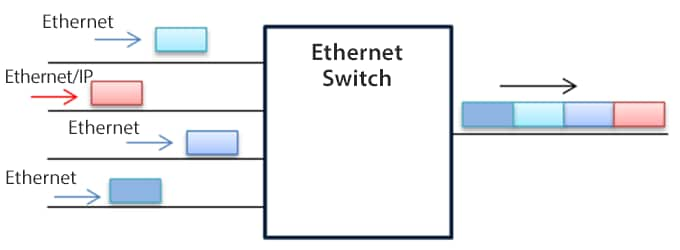
This function sends EtherNet/IP® packets first, regardless of the order of arrival at Ethernet switches.
EtherNet/IP® has two communication functions: implicit messaging which communicates in a fixed cycle, and explicit messaging which communicates at arbitrary timings.
This function communicates data in a cyclic manner (in a fixed cycle) determined with the requested packet interval (RPI), using implicit message communication as specified by EtherNet/IP®. The RPI can be individually set for each connection, allowing for communication with devices that communicate at different speeds. In cyclic communication, data is communicated between devices when one device successfully opens a logical communication line, called a connection, to the other device.
There are two types of connection: Exclusive Owner which allows both transmission and reception, and Input Only which allows only transmission. Input Only is more commonly used. When devices both send and receive using Input Only connections, both devices need to open a connection to the other one.
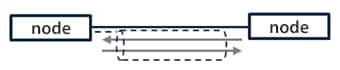
Data can be transmitted and received when one node opens a connection.
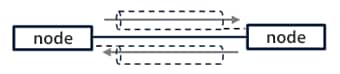
Data can be transmitted and received when both nodes open a connection to each other.
The communication ability of EtherNet/IP®-compatible devices is expressed using pps. pps stands for packets per second, which means the number of packets that can be sent and received per second. Receiving data from a device with an RPI of 1 ms means that approximately 1000 packets are required per second (1000 pps). Therefore, a device with 10000 pps can communicate with 10 devices with an RPI of 1 ms.
Connections that can be configured with each device are described in EDS files. Connections can be opened with simple operations by registering the EDS files prepared by EtherNet/IP®-compatible device manufacturers.
This communication method performs one-to-one data communication with a specified node at arbitrary timings. This method allows transmission and reception from devices that cannot be performed with implicit message communication.
EtherNet/IP® can also use data communication via general-purpose Ethernet, allowing for simultaneous communication of file exchange using the File Transfer Protocol (FTP) or similar protocols.
This is an RS-485 based open network using CIP.